As you know, Blockchain has revolutionized the way we transfer and store data, providing a secure and decentralized platform for recording transactions.
At the heart of this technology is the concept of layers, which refers to the different components and functions that make up a blockchain system.
In this article, we will explore the layers of a blockchain and how they work together to create a secure platform for recording and verifying transactions.
So before moving on let's get to know about the content of the article.
Blockchain Trilemma
CAP Theorem
Layers
Bitcoin Lightning Network
Blockchain Trilemma
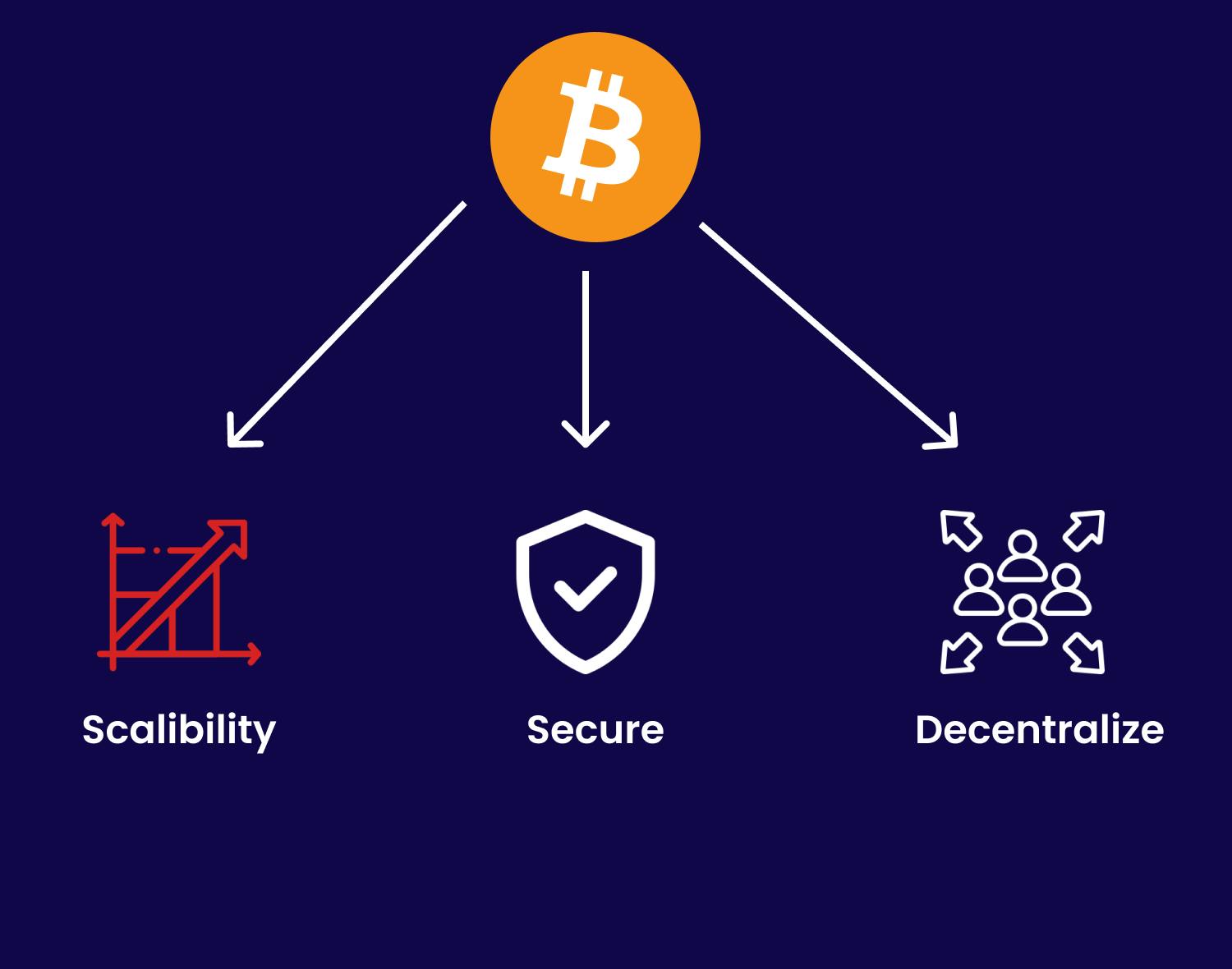
The blockchain trilemma is a term used to describe the three key characteristics that define a true blockchain: scalability, security, and decentralization. In order for a system to be considered a blockchain, it must possess all three of these attributes. The blockchain trilemma represents the fundamental trade-offs that must be made in order to create a secure and decentralized system that is also able to scale effectively.
Scalability: The number of transactions that can be processed per second.
Security: The safety and protection of the network.
Decentralization: The distribution of data across a decentralized network rather than a centralized system.

CAP Theorem
The CAP theorem states that in any distributed system, it is impossible to simultaneously achieve all three of the following goals: consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. In the context of blockchain technology, this means that it is not possible to fully optimize for all three pillars of the blockchain trilemma - scalability, security, and decentralization - at the same time. Instead, one must compromise on one of these pillars in order to achieve the others to their full potential. For example, if you prioritize scalability and security, decentralization may suffer. Alternatively, if you prioritize security or decentralization, scalability may be compromised. Understanding this trade-off is crucial for effectively designing and implementing a blockchain system.
For example, The Bitcoin network is not very scalable as it can only process around 7-8 transactions per second on average. This can cause delays in the confirmation of transactions, especially during times of high network demand. For example, if you make a transaction on the Bitcoin network, it may take an average of 10 minutes for it to be included in a block. However, for the transaction to be considered fully confirmed, it must be included in a certain number of subsequent blocks, which can take additional time. This is because the Bitcoin network follows the "longest chain rule," which means that the longest chain of blocks is considered the valid one. As a result, it may take upwards of an hour for a transaction to be fully confirmed on the Bitcoin network.
To address this issue, the concept of layers was introduced.
Layers
In blockchain technology, "layers" are the various components and functions that make up the system. These layers act as building blocks, each serving a specific purpose and contributing to the system's overall functioning.
There are several layers in a blockchain system:
Application layer: This is the topmost layer, where applications that interact with the blockchain are built. These applications may include cryptocurrency wallets, exchanges, and other financial applications.
Network layer: This layer consists of the nodes that make up the blockchain network. These nodes may include full nodes, which maintain a copy of the entire blockchain, and lighter-weight nodes, which may only store a subset of the blockchain.
Consensus layer: This layer is responsible for ensuring that all nodes on the network reach a consensus on the state of the blockchain. This is typically done through the use of a consensus algorithm, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake.
Ledger layer: This layer is where the actual transactions and blocks are stored. Each block contains a record of multiple transactions, as well as a cryptographic hash of the previous block in the chain. This creates a secure, tamper-evident record of all transactions on the blockchain.
Blockchain Layers Explained

Layer 0
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 0
Layer 0 is the foundation of the blockchain that allows blockchains to interact with each other and provides the infrastructure for developers. It requires various components, including the internet, hardware, and various connections, to make the blockchain functional.
Layer 1
Layer 1 is an improvement on the foundation (Layer 0) of the blockchain. It helps the blockchain network work properly, but it has limits on how much it can grow. If there are problems with the new rules (protocol) in Layer 0, they can also affect Layer 1. Layer 1 is also known as the implementation layer. Some examples of blockchains that use Layer 1 are Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, and Ripple.
Layer 2
Layer 2 is the most important layer of the blockchain because it addresses scalability. Many blockchains, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, and Ripple, have strong foundations (Layer 0) and security (Layer 1), but they struggle with scalability. Layer 2 is a solution for specific blockchains that helps them scale by integrating with third parties and overcoming the limitations of Layer 1. It is currently the most popular way to solve scalability issues in proof-of-work (POW) networks. Many industries are now implementing Layer 2 technologies.
For example, Polygon uses Layer 2 solutions to improve the scalability of the blockchain, making it faster. Similarly, the Bitcoin Lightning Network, which we will discuss later, is a Layer 2 solution for the Bitcoin blockchain.
Layer 3
Layer 3 blockchain is also known as the application layer. It is responsible for hosting decentralized applications (DAapps) and other protocols that allow other apps to work. It is divided into two main sub-layers: application and execution. Layer 3 is the most powerful solution for connecting different blockchains and achieving true interoperability.
Bitcoin Lightning Network
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is not the only solution for improving the scalability of the Bitcoin network. Before Layer 2 solutions were developed, developers tried other methods to increase scalability.
One solution was to increase the size of the blocks in the Bitcoin blockchain. This would allow more transactions to be included in each block, increasing the number of transactions processed. However, this solution has a downside: if the block size is increased, it will take longer to distribute the block across the decentralized network because the size of the data being transmitted also increases.
Another solution was to store some data off-chain and some on-chain, with transaction data stored on-chain and other data stored on centralized servers. However, this solution has the problem that the data stored on centralized servers can be changed or manipulated. Despite this issue, some companies still use this method.
When these solutions failed to increase the scalability of Bitcoin, another solution called the Bitcoin Lightning Network⚡ was introduced.
Bitcoin Lightning Network was published by researchers Thaddeus Dryja and Joseph Poon in 2015. It is the layer 2 solution to increase the scalability of Bitcoin. It makes bitcoin more scalable. Now, you might be wondering, how?
Before we continue, let's clarify what the Bitcoin Lightning Network is not. You may have doubts that it is a new blockchain or a separate cryptocurrency. However, that is not the case. The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a program or protocol that uses Layer 2 solutions to make Bitcoin more scalable.
Working of Bitcoin Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain that allows for faster, cheaper transactions between participating nodes. It does this by creating a network of "payment channels" between nodes that can be used to conduct multiple transactions without the need for each one to be recorded on the blockchain.
Here's how it works:
Two parties (nodes) who want to transact with each other open a payment channel, which is essentially a smart contract that holds a certain amount of bitcoin.
To start a payment channel, both parties must commit an amount of Bitcoin. That Bitcoin is held and cannot be released as long as the payment channel remains open. The total amount of Bitcoin that can be transferred through this channel is the total amount of Bitcoin committed.
Let’s look at an example: John and Charles want to form a payment channel with each other. John commits 15 BTC and Charles commits 15 BTC to the payment channel. An opening transaction holding John and Charles’s combined 30 BTC is put onto the Bitcoin blockchain. Once that transaction has been added to the blockchain, which can take 10 minutes or more, John and Charles can transact an unlimited number of times at much faster speeds and effectively zero cost. Below are transactions between John and Charles:
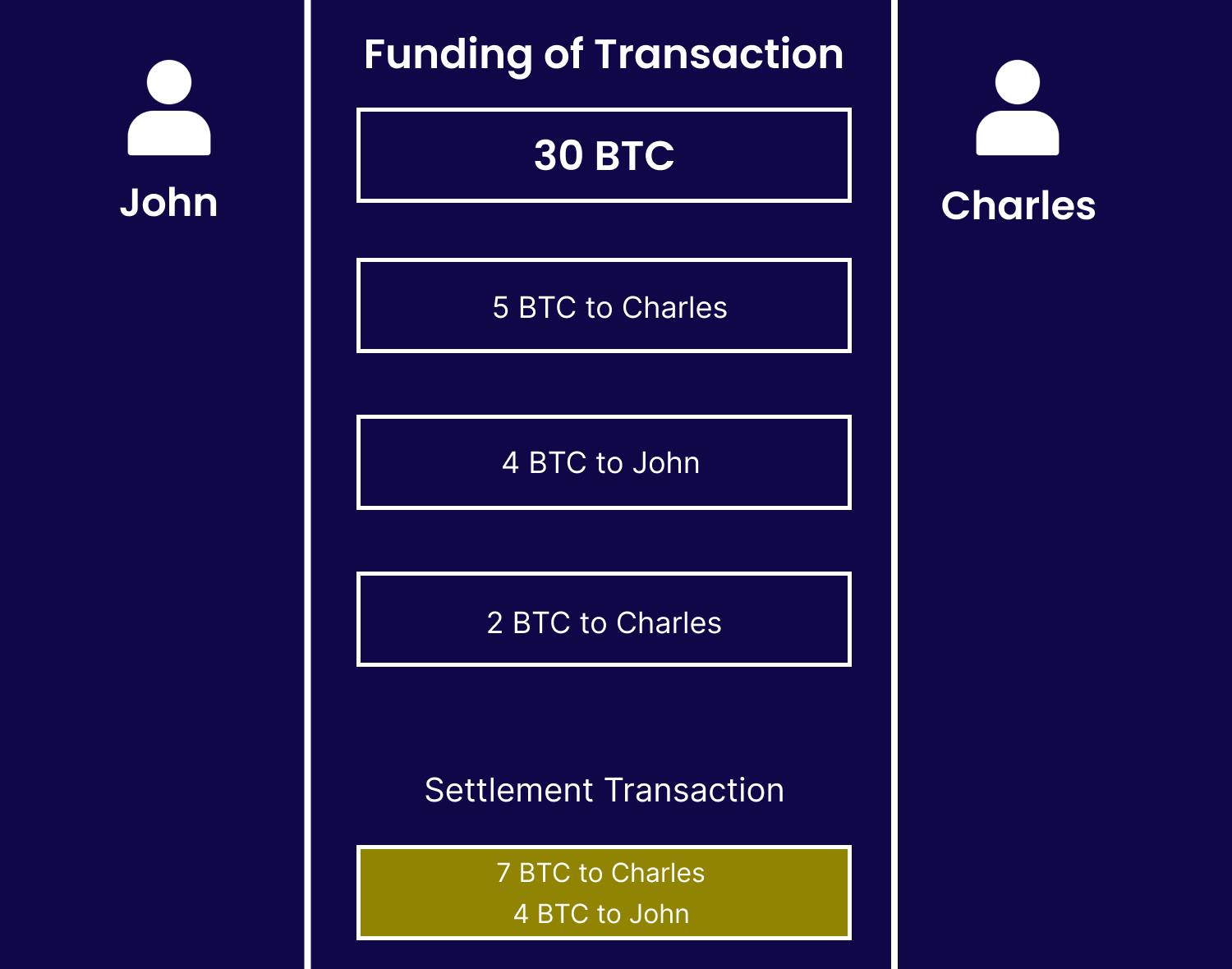
John sends Charles 5 BTC John: 10 BTC Charles: 20 BTC
Charles sends John 4 BTC John: 14 BTC Charles: 16 BTC
John sends Charles 3 BTC John: 11 BTC Charles: 19 BTC
When two people, John and Charles, are using a payment channel in the Bitcoin Lightning Network and they want to stop using the channel, they can send a closing transaction to the Bitcoin blockchain with their final balances. This means that they will record on the blockchain how much Bitcoin each person has at the end of their transactions through the payment channel. In the example you provided, John has a final balance of 11 BTC and Charles has a final balance of 19 BTC.
The Lightning Network (LN) is a new protocol that is still being tested and developed. It has many challenges to overcome, including issues with usability and security. These challenges may affect how well the LN works and how safe it is to use.
To learn more about the Bitcoin Lightning Network, visit the website bitcoin.com/get-started/what-is-lightning-n... This resource contains a wealth of information about the Lightning Network, including its purpose, how it works, and its benefits.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article. I hope that you have gained a better understanding of the Layers and Bitcoin Lightning Network and its potential to revolutionize the way we use Bitcoin. I appreciate your interest in the topic and hope that you found the information provided to be informative and useful.
